Podiatric and Diabetic Foot care focuses on preventing, diagnosing, and treating foot-related problems—especially in people with diabetes. Feet are often ignored until pain, wounds, or infections show up, and by then, damage may already be serious. Diabetes reduces blood flow and nerve sensation, making even small cuts risky. Modern podiatric care is not just about wound treatment; it’s about early detection, pressure management, infection control, and limb preservation. With the right care at the right time, most diabetic foot complications are preventable. The goal is simple: protect mobility, prevent amputations, and keep patients walking confidently.
This specialty addresses a wide range of foot and ankle problems, with special focus on diabetic patients.
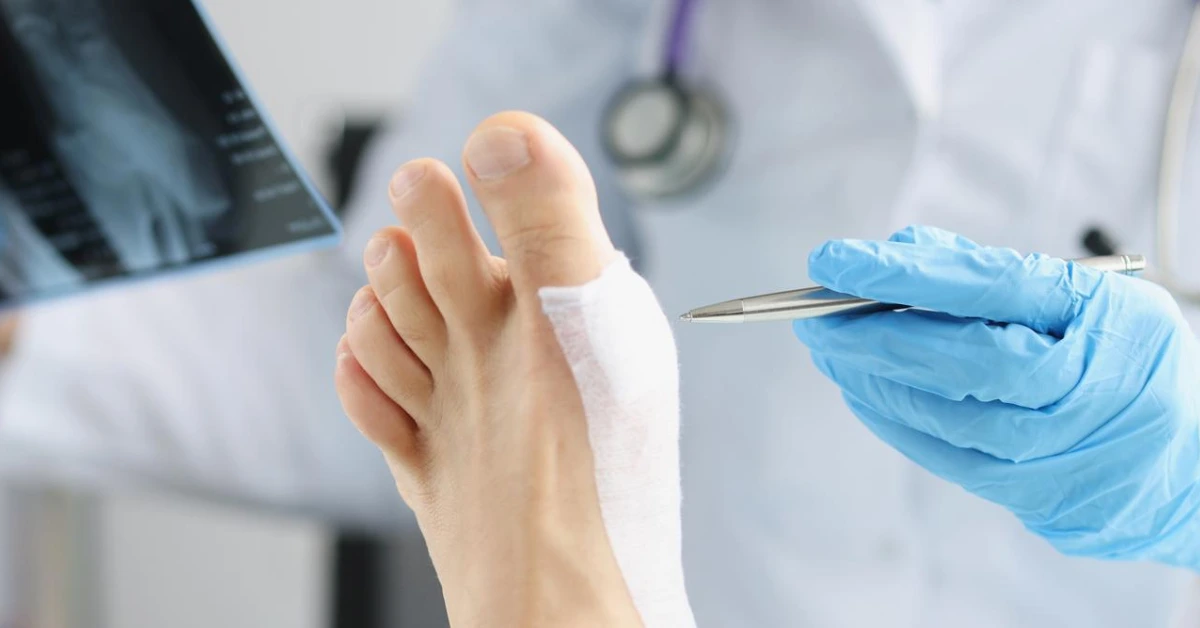
Diabetic foot problems often progress silently.
Accurate assessment is critical to saving the foot—and sometimes life.
Treatment focuses on healing, prevention, and long-term protection.
Delaying foot care can cost more than time—it can cost a limb.
Early care = limb-saving care.
Preparation improves treatment safety and results.
Aftercare is essential to prevent recurrence.
Small daily habits make a massive difference.
Consistency saves feet—literally.
Foot care works best with overall diabetes control.
Foot health = overall health.
Podiatric and Diabetic Foot care is a critical part of diabetes management—not an optional add-on. Most foot ulcers, infections, and amputations are preventable with early detection, proper treatment, and consistent care. Ignoring foot symptoms can lead to severe complications, while timely intervention protects mobility and quality of life. At MAHI Hospitals, podiatric and diabetic foot care is delivered with a preventive, limb-saving approach—combining expertise, advanced wound care, and patient education to help individuals stay active, independent, and confident on their feet.
Diabetic patients should get a foot check at least once a year, or immediately if there is numbness, wounds, color change, or pain. Early care prevents serious complications.
Yes, most diabetic foot ulcers heal well with early treatment, proper wound care, pressure offloading, and blood sugar control. Delays increase complication risk.
Absolutely. Daily foot inspection, proper footwear, controlled blood sugar, and regular podiatric visits significantly reduce the risk of ulcers and amputations.
Fill out the form and our patient care coordinators will get back to you within 24 hours to assist with appointments, queries, or any guidance you need.